5.17.2.2 IBuffer Filtering ¶
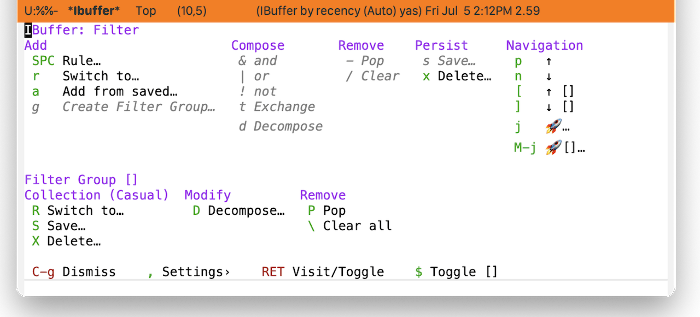
IBuffer is embarrasingly rich in the ways it can filter buffers. Once mastered, IBuffer filtering offers a way to create different views on your buffer list, enabling you to tailor bespoke views for different workflows. Such capability comes with a price though: you’ll need to understand how IBuffer wants to organize filters.
Key is the concept of a Filter Group which is IBuffer’s analog to a Dired subdirectory ((emacs)Subdirectories in Dired). But whereas a subdirectory only maps to a file system directory, a filter group can be constructed from a diverse set of rules to categorize a buffer.
IBuffer organizes filtering with the following taxonomy:
- Filter rule
The smallest unit of filtering. There are many types of filter rules:
- filter by major mode
- filter by derived mode
- filter by buffer name
- filter by buffer content
- filter by basename
- filter by directory name
- filter by filename
- filter by file extension
- filter by modified buffers
- filter by an arbitrary Lisp predicate
- filter by buffer size
- filter by special buffers
- filter by buffers visiting files
Casual IBuffer makes the design decision to not enumerate the above in a menu, delegating the work of filter selection to the command
ibuffer-filter-chosen-by-completion.
- Filter
A filter is a logical combination of filter rules. Logic operators such as AND (&), OR (|) and NOT (!) are used to compose rules into a filter. A single filter rule can also be construed as a filter.
Properties of filters:
- A filter can be defined and saved for subsequent use.
- Filters are saved in the customizable variable ‘ibuffer-saved-filters’.
- Multiple filters can be applied at the same time to a set of buffers.
- Multiple filters are applied in LIFO order. Removing a filter is a “pop” operation.
- Rules that are combined with a logic operator are treated as a single element of the LIFO stack.
- To individually edit the combination, use the Decompose command to remove the logic operator first.
- A filter can be defined and saved for subsequent use.
- Filter Group
A filter group is set of filters. The set itself is named with an identifier that is user-defined.
Properties of filter groups:
- A filter group can be defined and saved for subsequent use but with a special qualifier:
- Filter groups are only saved as a collection (more below) in the customizable variable ‘ibuffer-saved-filter-groups’. A filter group can not be saved individually.
- Multiple filter groups can be applied to partition the buffer list.
- Multiple filter groups are applied in LIFO order. Removing a filter group is a “pop” operation.
- Similar LIFO and decompose behavior applicable to a filter group is supported.
- A filter group can be defined and saved for subsequent use but with a special qualifier:
- Filter Group Collection
A collection is a set of filter groups that can be named with a user-defined identifier. Only one collection can be applied to a buffer list at a time. However, many different collections can be defined, allowing for different views of the same buffer list.
Creating Filters
The basic procedure for making a filter that applies to the entire buffer list is as follows:
- From the Filter menu, create a filter via (SPC) Rule… and some desired combination of operators.
- Save the filter via (s) Save…. You will be prompted to provide a name for the filter. This filter will be saved in the variable ‘ibuffer-saved-filters’.
- To recall this filter at a subsequent time, use (r) Switch to… in the Add section of the Filter menu.
Creating a Collection of Filter Groups
Here is where the taxonomy becomes significant as the IBuffer command set unfortunately does not provide much observability on edit operations to filters.
- Create a filter as described above.
- In the Add section of the Filter menu, select (g) Create Filter Group… to convert the filter into a filter group. You will be prompted to name the filter group. This group name will be enclosed by square brackets [].
- Multiple filter groups can be created by repeating steps 1 and 2 above. Note that when constructing a filter group, the IBuffer window will not provide observability of existing filter groups on the buffer list.
- You can save the set of filter groups as a collection in the Collection section with the command (S) Save…. You will be prompted to name the collection. Note that only one collection can be used at a time in IBuffer.
Out of the box, it is best to think of the IBuffer commands for editing buffer filters as a kit of parts and an arguably incomplete one at that. The Casual IBuffer filter menu (‘casual-ibuffer-filter-tmenu’) is my attempt to build a comprehensible filter editor UI from this kit. Whether it succeeds in being comprehensible is left to user feedback.